Process automation is the use of various technologies to run business processes or routine tasks in place of manual effort. It involves using proven software tools and applications, software bots, and other digital systems.
The goal is to reduce human intervention while increasing business operations' efficiency, consistency, and reliability. Software tools will achieve this with little to no coding needed.
This article will discuss different types of process automation, their benefits, and examples. This will help you choose the best automation type for your business scenario.
Let's begin.
Types of Process Automation
Let's discuss the common process automation types that are in use today. All types offer general benefits like efficiency, cost savings, accuracy, consistency, and scalability. So, we will discuss the unique benefits of each process automation type.
Business Process Automation (BPA)
Business Process Automation (BPA) involves technologies for automating repeatable tasks of a business process. BPA aims to simplify business operations by reducing manual tasks in one or more business processes.
BPA is cross-functional and involves multiple steps, departments, or systems. It is more than a simple task automation. Its scope is to improve the overall efficiency and effectiveness of business processes. BPA ends when the entire business process is automated and optimized.
Unique Benefits of BPA
-
Quick Deployment: Create business process systems done in weeks, not months or years.
-
Efficiency: Automates routine tasks that involve one or more departments within an organization.
-
Consistency: Ensures business processes are performed the same way every time.
-
Compliance: Helps maintain adherence to regulatory requirements by standardizing processes.
Examples of BPA Tools
- Kissflow
-
Description: A low-code/no-code platform for building, deploying, and managing enterprise-grade apps for your business processes.
-
Features: Graphical designer for forms, process flows, and user permissions to create apps for business processes.
-
- Nintex
-
Description: A platform for optimizing business processes with forms, workflows, and AI.
-
Features: Focused on BPA and Workflow Automation with some RPA capabilities built in.
-
Examples of Business Process Automation
-
Automating employee onboarding processes.
-
Simplifying procurement from request to approval to payment.
-
Managing travel requests from start to finish.
-
Request for petty cash.
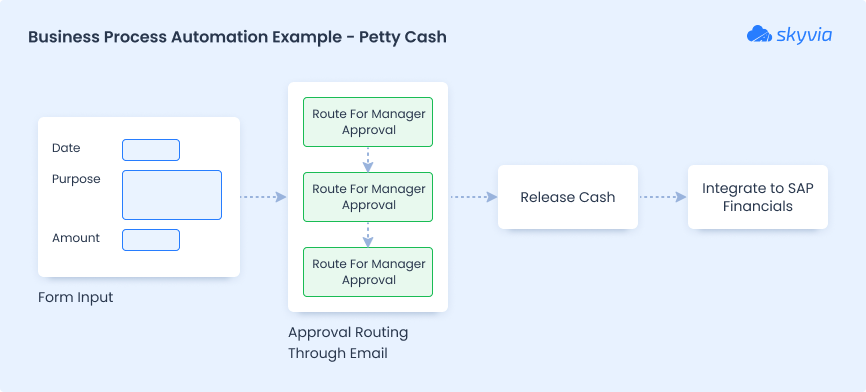
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) involves using software bots to do repetitive manual tasks. These bots can mimic human actions like clicking, typing, and navigating through applications.
RPA does not refer to mechanical robots like those in science fiction films.
Unique Benefits of RPA
-
Interface with Legacy Systems: Allow bots to do data entry tasks in legacy systems where integration is hard or impossible.
-
Increased Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks typically done by humans like data entry tasks. This allows employees to focus on higher-value activities.
-
Scalability: Easily scales operations by adding more bots as needed.
-
Quick Implementation: Rapid deployment without needing extensive changes to existing IT infrastructure.
Examples of RPA Tools
- UiPath
-
Description: A leading RPA platform that enables organizations to automate repetitive tasks.
-
Features: Drag-and-drop workflow design, AI integration, extensive pre-built automation components.
-
- Automation Anywhere
-
Description: An RPA platform that provides intelligent automation solutions.
-
Features: Focused on BPA and Workflow Automation with some RPA capabilities built in.
-
Examples of Robotic Process Automation
-
Automating data entry in financial systems.
-
Automated entry and processing of insurance claims.
-
Managing customer service tickets.
Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning Automation
AI/ML automation involves technologies for automating complex tasks requiring cognitive abilities. Such abilities include predictive analytics, decision-making, and data analysis.
Unique Benefits of AI/ML Automation
-
Enhanced Decision-Making: Offers data-driven insights for better decision-making to complete tasks.
-
Predictive Analytics: Makes predictions about patterns and results by analyzing historical data.
-
Improved Accuracy: Uses cutting-edge algorithms to cut down on errors.
-
Personalization: Enables customized user experiences and recommendations.
-
Scalability: Handles complex computations and massive amounts of data.
Examples of AI/ML Automation Tools
- Google Cloud AI
-
Description: A suite of AI tools and services from Google Cloud.
-
Features: Pre-trained models, custom model training, and integration with other Google Cloud services.
-
Use Case: Speech and image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics.
-
- IBM Watson
-
Description: An AI platform that offers a range of cognitive computing capabilities.
-
Features: Natural language processing, machine learning, data analysis, and integration with various applications.
-
Use Case: Chatbots, customer sentiment analysis, and fraud detection.
-
Examples of AI/ML Automation
-
Chatbots for customer support.
-
Credit card fraud detection.
-
Personalized marketing campaigns.
IT Process Automation (ITPA)
This type of process automation is used to manage and streamline IT operations and administrative tasks. The aim is to decrease manual labor, increase productivity, and strengthen the dependability of IT services.
Unique Benefits of ITPA
-
Incident Response: Speeds up incident detection and resolution.
-
IT Support: Improves management of support tickets and service management.
Examples of ITPA Tools
- ServiceNow
-
Description: A cloud-based platform that offers IT service management and automation solutions.
-
Features: Incident management, change management, asset management, and workflow automation.
-
Use Case: Automating ticketing systems, change approvals, and IT asset tracking.
-
- BMC Helix
-
Description: An ITPA platform that provides intelligent automation solutions for IT operations.
-
Features: AI-driven analytics, workflow automation, and real-time monitoring.
-
Use Case: Automating incident resolution, patch management, and performance monitoring.
-
Examples of IT Process Automation
-
Incident Management Automation: Automatically detecting and resolving incidents can drastically reduce downtime and improve system reliability. By automating responses to common issues (e.g., restarting services or rebooting servers), organizations can maintain high availability and reduce the workload on IT teams.
-
Patch Management Automation: Keeping systems and software up-to-date with security patches is critical for protecting against vulnerabilities. Automating patch management ensures timely updates across all systems, reducing the risk of security breaches and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
-
User Account Management Automation: Automating tasks like account creation, modification, and deactivation streamlines user management, enhances security by enforcing access control policies, and reduces the administrative burden on IT teams, particularly in large organizations.
Workflow Automation
Automating the flow of tasks and information, including documents, across various business processes is the job of Workflow automation. Simplifying workflows and improving collaboration are among the goals of workflow automation.
Unique Benefits of Workflow Automation
-
Collaboration: Enhances collaboration by providing a centralized platform for workflow management.
-
Visibility: Provides real-time visibility into workflow status and performance.
Examples of Workflow Automation Tools
- Microsoft Power Automate
-
Description: Microsoft's cloud-based service for creating automated workflows between applications and services.
-
Features: Includes templates for common automation. It has deep integration within the Microsoft ecosystem. There’s also an AI builder for complex tasks.
-
- Skyvia
-
Description: A 100% cloud data platform for many integration needs with workflow automation built-in.
-
Features: Drag-and-drop workflow design with triggers and actions. Integrates with hundreds of apps, cloud storage, databases, and data warehouses.
-
Examples of Workflow Automation
-
Automating the approval process for expense reports.
-
Managing marketing campaign workflows.
-
Upload and process CSV file then inform user of results.
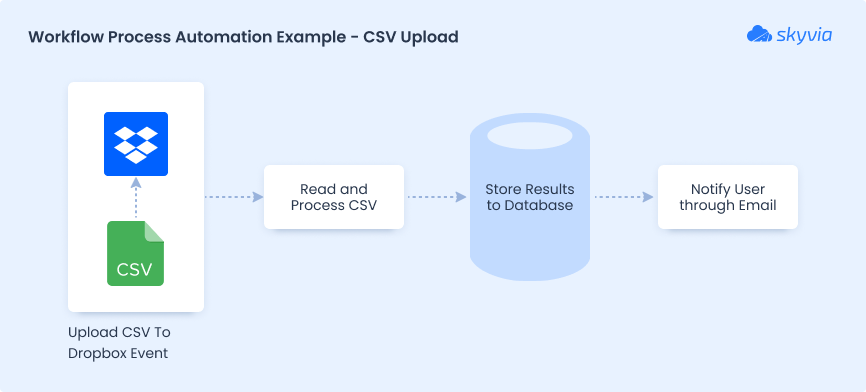
Integrated Process Automation (IPA)
Integrated Process Automation (IPA) combines traditional automation technologies with advanced AI and machine learning to create end-to-end automated solutions. Automating complex processes that involve multiple systems and need cognitive abilities are among the goals of IPA.
Benefits of IPA
-
End-to-End Automation: Automates entire processes, reducing manual intervention.
-
Combined process automation capabilities: Combine the benefits of BPA, RPA, AI/ML, and workflow automation.
-
Flexibility: Adapts to changing business needs and environments with various automation types. Use the process automation types that make sense to a business problem.
IPA Tool Example
- AutomationEdge
-
Description: An IPA platform that combines RPA with AI, ITPA, BPA, and workflow automation to automate complex business processes.
-
Features: Machine learning, natural language processing, and integration with various systems. Targets various industries like health care, IT, Insurance, banking, and more.
-
Examples of Integrated Process Automation
-
Automating end-to-end loan processing in banks.
-
Integrating supply chain operations.
-
Automating insurance policy management.
Process Automation Types Table of Differences
All types of process automation can be confusing to differentiate. Even tools and process automation solutions may overlap the types. Here's a table of differences for all types discussed.
| Type | Description | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business Process Automation (BPA) | Automates entire business processes from start to finish. | To improve efficiency and effectiveness of complete business processes. | Automating procurement processes from order creation to invoice approval. |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Automates repetitive tasks within applications or across systems. | To replace manual, repetitive tasks with software bots. | Automating inputs of data in a legacy insurance system. |
| AI/ML Automation | Uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate tasks and decision-making. | To enhance automation with advanced data analysis and learning capabilities. | Predictive maintenance for machinery based on historical performance data. |
| IT Process Automation (ITPA) | Automates IT operations and administrative tasks. | To improve efficiency and accuracy of IT management and operations. | Automating server backups and patch management. |
| Workflow Automation | Automates sequences of tasks across multiple systems. | To streamline and automate business workflows. | Automatically creating a support ticket when a new email arrives. |
| Integrated Process Automation (IPA) | Combines various workflow automation types to manage complex processes involving multiple systems. | To integrate and automate end-to-end business processes. | Managing an entire customer onboarding process from form submission to Salesforce entry and follow-up emails. |
General Steps in Implementing Any Process Automation Type
Each type of process automation has unique capabilities. However, the steps in making process automation work are generally the same.
Here they are:
- Identify a manual task or process to automate.
- Analyze the steps needed from start to finish. Identify the inputs and outputs of each step. Consider integration, security, compliance, and maintenance. Document your analysis.
- Choose the best process automation type and tool to address the manual task or process.
- Design and configure the steps using the chosen process automation tool.
- Test the automation, correct, and adjust as needed.
- Deploy the process automation.
- Monitor the performance and adjust as needed.
Process Automation Pain Points and Solutions
Process automation can be a challenging project for your organization. But the benefits outweigh the challenges and there are solutions for every challenge.
Whether it's BPA, RPA, or any type, a solution to a challenge is available. Check them out below
- Complexity of Integration
-
Pain Point: Integrating process automation tools with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming. Legacy systems add more to the challenge because of the absence of application programming interfaces (APIs).
-
Solution: Use platforms with robust integration capabilities and pre-built connectors that your company needs. Work with experienced implementation partners for seamless integration.
-
- Change Management
-
Pain Point: Employees may resist changes to their work and fear losing their jobs.
-
Solution: Involve management and employees in the automation process to ensure buy-in and smooth transition. Provide training and communicate the benefits of process automation.
-
- Security and Compliance Risks
-
Pain Point: Automating processes that handle sensitive data can introduce security and compliance risks.
-
Solution: Use process automation tools that comply with industry standards and regulations. Implement strong security measures such as encryption and access controls. Perform regular audits.
-
- Initial Cost and ROI Concerns
-
Pain Point: The upfront cost of implementing automation can be high. The return on investment (ROI) may not be realized sooner.
-
Solution: Start with automating high-impact processes that offer quick wins. Measure and communicate the ROI through improved efficiency, cost savings, and other KPIs.
-
- Maintenance and Updates
-
Pain Point: Automated processes need ongoing maintenance and updates to remain effective.
-
Solution: Assign a dedicated team to maintain and update automations. Use tools that offer easy modification and scaling capabilities.
-
- Learning Curve
-
Pain Point: Learning various process automation techniques can be difficult and time-consuming.
-
Solution: Use platforms that offer easy user interfaces and solutions. It should also provide extensive documentation and training.
-
AI/ML Automation Challenges and Solutions
Adding AI and ML to the mix introduces new challenges:
- Data Quality
-
Pain Point: Poor data quality adds to model inaccuracy.
-
Solution: Robust data governance practices and clean, up-to-date data.
-
- Model Complexity
-
Pain Point: Developing and tuning complex models can be challenging.
-
Solution: Look for expert advice and tips for model development and use pre-built models.
-
- Ethical Considerations
-
Pain Point: Ensuring ethical use of AI and avoiding bias in models.
-
Solution: Make sure training data is diverse. Do regular audits and enforce ethical guidelines.
-
Future Trends in Process Automation
The future ahead of us is exciting because of more innovations that will boost employee productivity and simplify corporate procedures.
Take a look at them all below:
- Advanced AI Integration
-
Description: AI technologies like natural language processing (NLP) will continue to improve and be used to enhance automation techniques.
-
Impact: Automation solutions that are more intelligent and adaptive will impact work. Eventually it will become capable of understanding and responding to human language and complex data patterns.
-
- Autonomous Process Automation
-
Description: Development of automation systems that can learn by themselves. So, they can adapt and optimize themselves without human intervention.
-
Impact: Efficiency and effectiveness of automation solutions will level up. This will reduce constant human oversight and maintenance.
-
- Edge Automation
-
Description: This is automation at the edge of networks which means closer to where data is generated. It will reduce latency and improve real-time decision-making.
-
Impact: Next-level upgrade in performance and responsiveness of automation solutions.
-
- Integration with Internet of Things (IoT)
-
Description: IoT devices will participate in automation processes. This will boost business operations by using data from connected sensors and devices.
-
Impact: Various industries such as manufacturing and logistics will enjoy improved operational efficiency, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring.
-
- Ethical and Responsible Automation
-
Description: Automation solutions will not only improve efficiency but will be designed and implemented ethically. This will consider the impact of automations on jobs and society.
-
Impact: Improves communication and coordination between employees and automation solutions that will boost overall productivity and effectiveness.
-
- Enhanced Collaboration Tools
-
Description: Development of automation tools that facilitate better collaboration between humans and automated systems.
-
Impact: Improves communication and coordination between employees and automation solutions, enhancing overall productivity and effectiveness.
-
Conclusion
Process automation uses various technologies to run routine tasks and business processes and reduce manual effort. Different types of process automation ensure varied business problems across many industries are covered.
Process automation solutions and tools may offer one or more types that customers can mix to solve a business problem. Tools like Skyvia provide an easy-to-use interface to make process automation as easy as possible.
We hope that this article is a valuable resource for your process automation efforts and tool selection.